Various methods are used to obtain essential oils, depending on their intended use. These oils are typically obtained from dried or fresh plants through steam or hydrodistillation. Citrus fruit oils are obtained through squeezing, while organic solvents are extracted for industrial purposes. Additionally, perfumery relies on the traditional method of odorizing fats known as enfleurage.
Properties
Essential oils are derived from plants. Approximately 2000 oil-bearing plants are known worldwide, primarily found in tropical regions. Oils are present in various plant parts, such as flowers, stems, roots, seeds, and resin. They are obtained through steam distillation, cold pressing, or alcohol extraction. Essential oils are not soluble in water.
Benefits
Essential oils have many health benefits. Here is what they do:
- Antiseptic effect – essential oils have antiseptic effects on viruses, molds, yeasts, protozoa, and Gram-(+) and Gram-(-) bacteria. In addition, they work on bacteria resistant to some antibiotics. Antimicrobial activity increases with increasing oil concentration, but it mainly depends on the chemical nature of the leading ingredient. The most intense antibacterial effect is in oils that contain eugenol (cloves and cinnamon) and phenols (thyme, savory, oregano).
- Expectorant effect – this effect consists of the oil irritating the bronchial mucosa, which causes increased secretion of retained mucus. The most effective form of using the oil for this purpose is inhalation of pure oils or a mixture with physiological saline. Eucalyptus, pine, thyme, fir, anise oil – these are oils with expectorant properties.
- Spasmolytic effect – reducing the tension of smooth muscles, mainly in the digestive tract, and restoring proper peristaltic movements. Some oils stimulate the secretion of gastric juice and inhibit the multiplication of bacteria. Lavender, peppermint, fennel, caraway, and lemon balm oils have spasmolytic effects.
- Diuretic effect: This effect consists of increasing urine secretion. Juniper oil and lovage root oil have such properties.
Individual oils also have calming, antiviral, sleep-inducing, antiemetic, and anti-inflammatory properties.
Which One To Choose?
Essential oils must be 100% natural. Price variations reflect the amount of raw material needed for production. For instance, clove oil has a near 1:1 production ratio, while obtaining 100g of rose oil requires about 100kg of flowers. Price discrepancies may also stem from differences in product quality. Cheaper oils are often contaminated, derived from lower-quality or synthetic plants. As a result, they may lack active ingredients and only offer a pleasant fragrance.
Contraindications
There are several contradictions to using essential oils.
| Skin reactions | Savory, citronella, cumin, oregano, cinnamon, cassia, verbena, lemongrass, clove, thyme, all citrus oils |
| UV sensitivity | Verbena, cumin, yarrow, citronella, St. John’s wort, lemon balm, all citrus oils |
| Pregnancy and lactation | Burnet anise, dill, lavender-leaved sage, parsley, thyme, basil, verbena, marjoram, peppermint, juniper, bay leaf, tarragon, clary sage, rosemary, meadowsweet, wormwood, fennel, nutmeg, sage, hyssop savory, ginger, clove, yarrow, cedar, camphor, cumin, oregano, lavender, cinnamon |
| Children under six years of age | Field mint, eucalyptus, peppermint, curly mint, hyssop, burnet anise, cumin, camphor tree, sage, camphor, oregano, thyme, rosemary |
| Epilepsy | Burnet anise, fennel, nutmeg, rosemary, thyme, cedar, camphor, nutmeg sage, parsley, sage, hyssop, cypress |
| Hypertension | Rosemary, sage, thyme, juniper, hyssop |
| Asthma | Eucalyptus, camphor |
| Increased intraocular pressure | Citronella, verbena, lemon eucalyptus, lemongrass, lemon balm |
| Poisonous oils | Mugwort, costus, calamus, rue, sassafras, wormwood, bitter almond, southernwood, pennyroyal, savin juniper, black mustard, wintergreen, boldo leaves, bitter fennel, common tansy, thuja |
Ways To Use Essential Oils
In simple terms, aromatherapy involves introducing essential oils into the body through the respiratory tract or the skin. Importantly, it never involves oral administration. Therefore, aromatherapy occurs in various ways.
Inhalation
This is the simplest and least invasive form of aromatherapy. Active substances contained in essential oils reach the respiratory tract in low concentrations. Volatile fragrance compounds penetrate the nasal and lung mucosa and thus enter the bloodstream. Inhalation occurs in the classic way when the oil is on a material or when the oil is sprayed, which is becoming increasingly popular. Aromatherapy devices are designed to disperse essential oil molecules in the air, which produces a healing, fragrant mist.
Massage
Aromatherapy also uses all types of massage. The most important element is choosing the right essential oil. Plant extracts for aromatherapy should not be used without prior dilution, as they are highly concentrated products and can cause skin irritation.
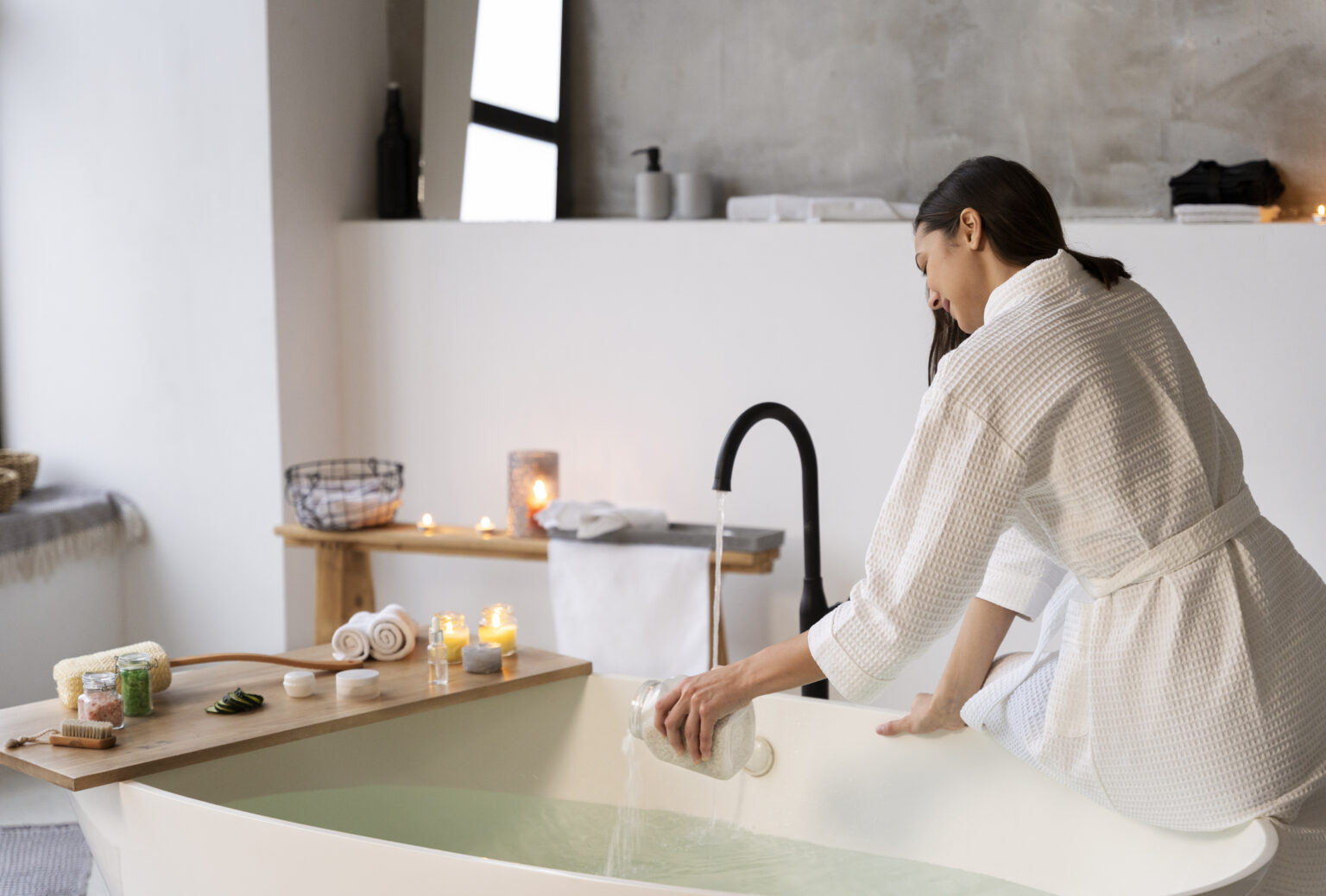
Bath
A bath with essential oils is also an excellent opportunity for an aromatherapy treatment. It is not only pleasant but also has healing properties. The most essential thing in this case is the water temperature, which should be around 40 degrees Celsius.
At this temperature, the skin pores expand, and the active substances of the oils are better absorbed and enter the circulatory system. In addition, in aromatherapy, we distinguish between a full bath, i.e., the whole body, and a local bath, i.e., just the hands or feet.
An aromatherapy bath should last about 20-30 minutes and should not involve detergents, foaming agents, or skin care products. At the end of the treatment, wipe your body dry; there is no need to rinse the skin.

Compresses And Poultices
Compresses or poultices are also used for aromatherapy. To do this, apply a few drops of essential oil to a cloth and apply it to the affected area. Temperature is significant in this case. Warm compresses are a suitable aromatherapy treatment for arthritis, inflammation, and aching muscles. Cold compresses, on the other hand, will be appropriate for relieving headaches, bruises, and tension. Hot and cold compresses can also be used interchangeably. They will bring relief, for example, in the case of injuries and bruises.
Other Ways
Essential oils are also added to hygiene products and skin care cosmetics; in these cases, regularity is the most important thing.
Where To Buy Essential Oils?
Buying essential oils is not a problem: they are available in online stores, drugstores, oriental stores, and even interior design stores or flower shops. However, you should always carefully check the composition of the product being sold – whether what the seller calls “natural” really is.
How To Start Working With Essential Oils?
Essential oils are obtained in various ways: by steam distillation, pressing, chemical extraction with organic solvents, and enfleurage technique. Oils should never be taken orally because they may burn the esophagus and internal organs. They can be applied to the skin but must be diluted with a base oil. Aromatherapy with natural oils can consist of inhalation, for which inhalers, diffusers, and burners will be needed. Another method is to massage the whole body or its specific parts. You can also use oils to make hot and cold compresses. They are great for bathing. They are also worth adding to cosmetics.
How To Use Them?
Due to their hormonal effects, pregnant women should avoid the following oils: cypress, hyssop, juniper, fennel, lavender, marjoram, lemon balm, peppermint, rosemary, rose, chamomile, sage, and thyme.
Before going out in the sun, the skin cannot be exposed to the following oils: bergamot, lemon, grapefruit, lime, mandarin, and orange.
Due to their high impact on the psyche, the following oils should be avoided in children: bergamot, tea tree, rosewood, eucalyptus, geranium, juniper, rosemary, sandalwood, nutmeg, sage, and thyme.
All types of essential oils should be used in small quantities due to their intensity. For example, pour 5 to 10 drops into an aromatherapy burner, 10 to 15 drops into a tub for a bath, and massage using 30 to 60 drops in 100 ml of oil.
When buying essential oils, you should be very careful. It is worth reading the label carefully. The natural raw materials listed in the composition must have the name, including the botanical name, of the plant from which they were obtained.
It is also worth noting that good-quality oils are usually not cheap. For this reason, some of them, especially the most expensive ones, such as rose oil or neroli, are diluted with vegetable oils or alcohol and sold in this form. Buy them in proven, trusted places, such as pharmacies.

Be Careful
There are some contraindications to the use of aromatherapy that you must consider before starting to practice it.
Essential oils are mixtures of many different substances. The more perfect our analysis methods, the more often we should consider the safety of using some products. Oils consist not only of health-promoting compounds. Some are potential allergens, and some components may even have toxic effects.
The International Fragrance Association
The International Fragrance Association, or IFRA, is primarily responsible for the safety of essential oil use. It specifies precise methods for testing fragrances, standards for their properties, and qualitative and quantitative profiles. Manufacturers must ensure that all this information is included on packaging and information leaflets.
26 substances have been classified as potentially hazardous. These are fragrance compounds that, especially in sensitive individuals, can cause contact allergies. If the concentration of any of these substances in the product exceeds 0.01%, this information must be included in the list of ingredients.
Remember to use essential oils in diluted form in everyday use. Under no circumstances should they be used in pure form—especially not on mucous membranes or damaged skin. Generally, do not exceed 30-60 drops per 100 ml of carrier. It is recommended that you follow the instructions carefully to avoid chemical burns.
Always, in the event of an undesirable event with an essential oil, remove it from the skin using oil-based cleaning agents. Then wash the skin with mild soap and rinse with warm water. Repeat if necessary. In the event of any disturbing skin symptoms, if the oil gets into the eye, or if too much of it is swallowed, seek medical help.
Essential oils should always be stored away from children and animals.
Allergy To Essential Oils
Before using a new essential oil, perform an allergy test. To do this, apply a few drops of the diluted product to the skin inside the forearm and observe the changes. Any redness or severe sensitivity of the application site indicates an allergic reaction. Sometimes, this happens immediately, and sometimes only after 24 hours. This means that this particular oil should be avoided.
A general safety rule is not to use essential oils from a plant that is an allergen for us – including food allergens.
Some oils, mainly citrus oils, have a phototoxic effect. This means that after exposure to the sun, a strong allergy similar to sunburn may appear on the skin. After applying such oils to the skin, you should refrain from exposure to sunlight for about 48 hours.
Sources
- Essential Oils. NIH.
https://www.niehs.nih.gov/health/topics/agents/essential-oils - Essential oils: a systematic review on revolutionizing health, nutrition, and omics for optimal well-being. NIH.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC10905622/ - Clinical Aromatherapy. NIH.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7520654/ - Inhalation Aromatherapy via Brain-Targeted Nasal Delivery: Natural Volatiles or Essential Oils on Mood Disorders. NIH.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9041268/ - Efficacy, Safety and Tolerability of Aroma Massage with Lavender Essential Oil: an Overview. NIH.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7043716/ - Essential Oils and Health. NIH.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32607090/ - IFRA Standards. IFRA.
https://ifrafragrance.org/docs/default-source/ifra-code-of-practice-and-standards/ifra-standards—48th-amendment/ifra-standards-in-full—booklet.pdf - Contact allergy to essential oils: current patch test results (2000-2008) from the Information Network of Departments of Dermatology (IVDK). NIH.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20946456/