- vitamin B1 (thiamine)
- vitamin B2 (riboflavin)
- vitamin B3 (niacin)
- vitamin B5 (pantothenic acid)
- vitamin B6 (pyridoxine)
- vitamin B7 (biotin)
- vitamin B9 (folic acid)
- vitamin B12 (cobalamin)
- egulating cholesterol levels
- regulating gene expression
- dilating blood vessels
- formation of erythrocytes
- regulating blood sugars
- Diarrhea
- Dermatitis
- Dementia
- Reduced muscle strength
- Depression
- Hallucinations
- Delusions
- For women, the daily dose of Niacin is 14 mg
- For men, the daily dose of Niacin is 16 mg
- For children, the daily dose of Niacin is from 5 mg to 11mg
- For pregnant women, the daily dose of Niacyn is 18 mg
- People who have a low-nutritional diet.
- People who frequently drink alcohol.
- People who have problems with vitamin absorption.
- People with high cholesterol.
- People who take antiepileptic drugs.
- People taking anti-tuberculosis drugs.
- People who are elderly.
- People taking small amounts of food.
- People who overuse sugar in their diet.
- Mirella Meyer-Ficca, James B Kirkland (2016). Advances in Nutrition, Niacin. https://academic.oup.com/advances/article/7/3/556/4616695
- Jonathan Prousky, Dugald Seely (2005). The treatment of migraines and tension-type headaches with intravenous and oral niacin (nicotinic acid): systematic review of the literature. https://nutritionj.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/1475-2891-4-3
- Institute of Medicine and Food and Nutrition Board (2001). Dietary reference intakes for vitamin A, vitamin K, boron, chromium, copper, iodine, iron, manganese, molybdenum, nickel, silicon, vanadium, and zinc. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK114304/
- Valeria Gasperi, Matteo Sibilano, Isabella Savini, Maria Valeria Catani (2019). Niacin in the Central Nervous System: An Update of Biological Aspects and Clinical Applications. https://www.mdpi.com/1422-0067/20/4/974
- Marc Beltrà, Noora Pöllänen, Claudia Fornelli, Kialiina Tonttila, Myriam Y. Hsu, Sandra Zampieri, Lucia Moletta, Samantha Corrà, Paolo E. Porporato, Riikka Kivelä, Carlo Viscomi, Marco Sandri, Juha J. Hulmi, Roberta Sartori, Eija Pirinen, Fabio Penna (2023). NAD+ repletion with niacin counteracts cancer cachexia. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-023-37595-6
- Sasa Redzic, Muhammad F. Hashmi, Vikas Gupta (2020). Niacin Deficiency. https://europepmc.org/article/nbk/nbk557728
- Wei Wang, Bo Liang (2012). Case report of mental disorder induced by niacin deficiency. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4198903/
Almost all B vitamins are not stored in the body. The only exception is vitamin B12. The rest, including Niacin, must be supplied to it regularly to prevent deficiencies and related diseases. The best source of these components is the diet. But supplementation is also possible. All B vitamins are water-soluble.
Functions of Niacin
Niacin is involved in many biochemical reactions related to energy production. Niacin is an essential element in many metabolic processes. Including the metabolism of fat, protein, or carbohydrates. In addition to it, Niacin also has other useful functions. Among others:

Niacin is an essential ingredient that we need regardless of age. The human body cannot produce enough Niacin on its own. So it is imperative to supply it with food. However, more and more studies are increasing the controversy over Niacin, and scientists also note its harmful effects. See what are the benefits and risks of vitamin B3 supplementation.
Niacin – benefits
Niacin is very beneficial for people. We need Niacin for proper metabolism. Vitamin B3 is an essential component of our diet. Its deficiency can cause various health problems. Many dangerous diseases can be prevented by taking care of proper niacin levels. Scientists have also noted that administering Niacin to patients can reduce the unpleasant symptoms of various diseases.

One such disease is migraine, the symptoms of which are sometimes very troublesome, and no medication helps. However, Niacin is effective. Oral or intravenous administration of Niacin makes the subcutaneous vessels dilate. It, in turn, removes acute migraine symptoms. Niacin can also prevent tension headaches.
Niacin deficiency
Vitamin deficiencies are very common. People nowadays live in a hurry and often do not have time to take care of their health. However, when the first symptoms of deficiencies appear, then it is essential to take matters into your own hands. Long-term deficiencies can be very dangerous to health and are the cause of various diseases.
Symptoms
Niacin deficiency can be diagnosed when alarming symptoms appear. Both physical and mental symptoms may appear. If you notice such a relationship in yourself, get your Niacin levels tested. Its long-term deficiency can cause the development of a serious disease. Therefore, we present the typical symptoms of vitamin B3 deficiency:
Diseases
Niacin deficiency can have consequences. You need to have a continuous supply of Niacin for the body to function correctly, and its lack can cause abnormalities. One of the dangerous consequences of niacin deficiency is pellagra disease. Pellagra can end in death, so that niacin deficiency can be dangerous. Completely different studies suggest that niacin deficiency can increase the risk of cancer. Therefore, taking care of proper niacin levels can counteract cancer cachexia. Niacin supplementation can also save you from cardiovascular disease or lung damage and positively affect mental health.
Treatment
To prevent unpleasant symptoms and diseases, it is necessary to ensure adequate levels of Niacin in the body. A disease such as Pelagra can be cured with oral supplementation of Niacin, which produces results in only two days. To maintain proper levels of Vitamin B3, specialists recommend a balanced diet. Niacin can be easily obtained in the food we eat. All we need to do is to make sure that our menus always include foods rich in Niacin.
Niacin and mental health
According to recent studies, there is growing evidence that Niacin positively affects neuronal health. Brain function is based on the work of neurons. Neurons are suitable for receiving and processing information that reaches the brain. Thanks to neurons, we feel, see, move and speak. Malfunctioning neurons can cause various mental disorders, such as Alzheimer’s Disease. Therefore, vitamin B3 deficiency can be dangerous to neuronal health, and it can cause damage and deficits. Researchers suggest that consuming the recommended dose of Niacin can promote neuronal health and protect against mental disorders and dementia.
Niacin – risks
Niacin is soluble in water. Therefore, it is quickly excreted from the body with urine. However, it is still possible to overdose on witamin B3. The effects of an excess of vitamin B3 include various symptoms. They can o be headaches, feelings of indigestion, or lack of appetite. But the most common are itching and redness of the skin. Unpleasant symptoms and side effects can occur when taking vitamin B3. But a slight overdose of Niacin is not a health risk. Symptoms disappear after a time when niacin levels regulate.
However, taking larger doses can cause permanent liver damage and the development of gout. Excess Niacin in the body should especially beware of pregnant women. Extra vitamin B3 significantly endanger their health and even causes congenital disabilities in the fetus. Long-term overuse of Niacin can cause vision problems.
In addition, a correlation has been noted between higher niacin supplementation and obesity and diabetes. Some researchers suggest that Niacin may raise glucose levels in patients with diabetes. Vitamin B3 may also increase the risk of developing diabetes in general.
What level of Niacin should you not exceed?
As you already know, Niacin has its wrong sides and many benefits. Its excess can harm the body, so it is better to monitor its levels. The body’s upper limit of vitamin B3 is 35 mg/d for adults. Thus high levels usually occur when people take Niacin in excess in supplements and diet. Fortunately, testing niacin levels is very simple. It is a preliminary medical test – a blood draw.
If you suspect you have an excess of Niacin, you can make an appointment to see your doctor and get it done with this basic test. Routine checkups are an excellent way to control Niacin levels. Such regular testing is recommended to be done at least once a year. Remember that it is always better to prevent diseases.
The daily requirement for Niacin
Vitamin B3 belongs to the group of water-soluble vitamins, which are better taken in smaller doses but more often, as excess is quickly removed from the body with urine. The daily reference requirement for Niacin varies depending on gender, age and condition. The daily intake of Niacin is as follows:
Children the younger they are, the less Niacin they should absorb per day, which is why there is such a large range. And pregnant women must be cautious of overdoses. Exceeding the upper dose of 35 mg results in side effects such as skin reddening.
What to eat to supplement Niacin?
A well-balanced diet should provide many vitamins, including niacin. It is useful to know which products contain a lot of niacin so that you do not end up deficient in it. After all, absorbing vitamins through food is the best way to do it. Find out what foods you should add to your menu to increase your vitamin B3 levels.
Vegetables and grains
When humanity was not yet developed enough to know the principles of healthy eating, pellagra epidemics were common. Populations whose diets relied on corn products were Niacin deficient. In contrast, people who included nuts and legumes in their diets had no problems with pellagra epidemics.
Thus, we find vitamin B3 in products such as beans and peas. And also sunflower seeds, peanuts, and lentils. Whole-grain bread is also a good source of Niacin.
Fish and meat
But the ideal source of vitamin B3 is protein-rich foods such as fish and meat. Chicken breast and tuna have the highest amount of Niacin. Veal, turkey, beef and pork offal, and mackerel also have large amounts of vitamin B3. Vegans can get large quantities of Niacin from plant foods such as bran and legumes. Besides, niacin supplementation is always available.
Herbs
Also, in herbs, we can find vitamin B3. It includes nettle, chamomile, or mint. You have to constantly take Niacin with your diet, considering that it is a water- and alcohol-soluble vitamin. Long cooking and processing of a meal significantly reduce the content of these compounds. Vitamin absorption is also much lower when drinking alcohol.
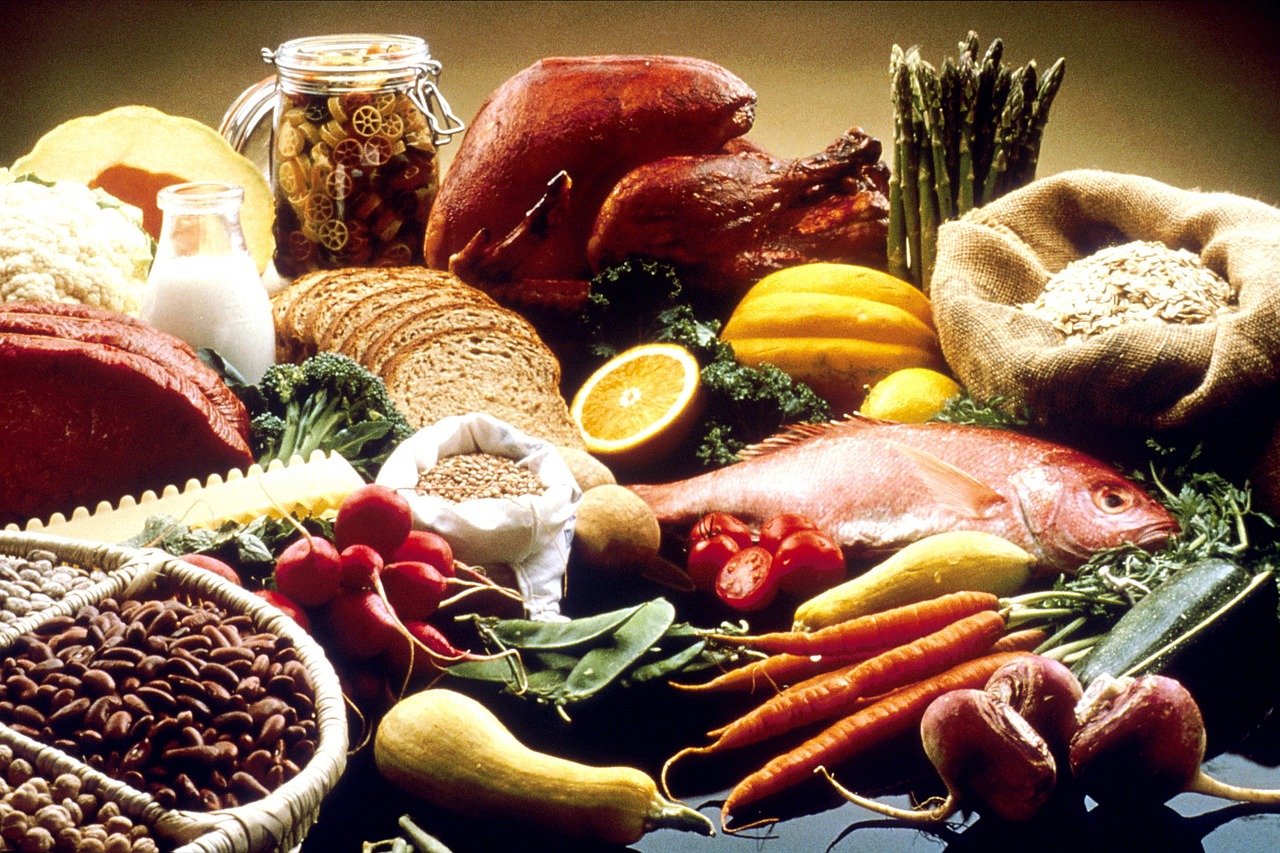

Who should supplement Niacin?
Some people are more prone to niacin deficiency, so they need supplementation. An unhealthy diet, unhealthy lifestyle, cigarettes, and alcohol – can all affect vitamin deficiencies. In addition, there are other situations in which vitamin B3 deficiency can occur. See which people, in particular, may need to take Niacin orally.
If you belong to any of these groups, you’d better take care of your niacin levels. As we mentioned, you can quickly test your niacin levels with a blood test. Sticking to proper niacin levels is essential and can protect you from many diseases and unpleasant ailments.
Summary
Maintaining good health is guaranteed by a varied and well-balanced diet. People need a constant supply of vitamins for the body to function properly. Niacin is an essential ingredient, and it has many beneficial properties, especially supporting metabolism and protecting people from Pellagra.
Most people get enough Niacin for their bodies with food, but additional supplementation may be necessary for severe deficiencies. But you also have to watch out for niacin overdose. Thus, all excess vitamins can cause side effects and other risks. It is best to start supplementation after consulting your doctor.
Sources
- Vitamin B3: Benefits, Dosage, and Risks
- What is Niacin?
- Functions of Niacin
- Niacin – benefits
- Niacin deficiency
- Niacin and mental health
- Niacin – risks
- What level of Niacin should you not exceed?
- The daily requirement for Niacin
- What to eat to supplement Niacin?
- Who should supplement Niacin?
- Summary









