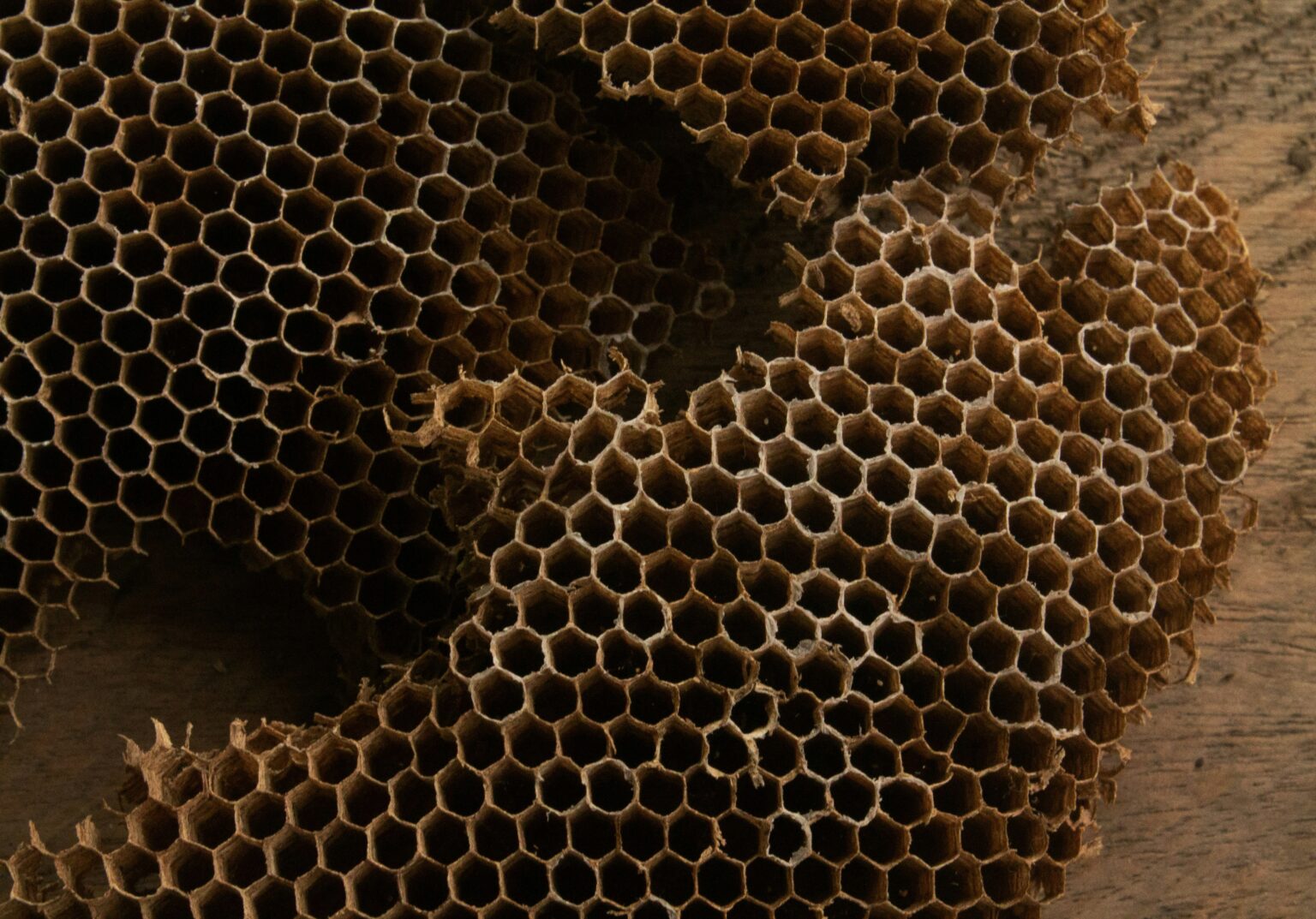
The title could be a compound of the Greek words “trypa,” which suggests a gap, and “phobos,” which implies fear. The disturbances of the structure can shift broadly between individuals; for a few, the triggers are bothersome, indeed, when they are as it were considering them. The pictures of the objects appear as lotus seed clusters, honeycombs, and human skin cavities.
Indeed, even though more than one-fifth of individuals suffer from trypophobia, it isn’t a recognized disorder in symptomatic manuals such as the DSM-5. A fear is ordinarily thought of as a non-authorized marvel of logical skill even though its status remains equivocal. But, this does not infer that it isn’t a considerable issue for the individuals managing it. It is said that the lion’s share of trypophobia patients report that their side effects, which incorporate uneasiness and shock, are so serious that they anticipate them from doing their day-by-day exercises.

What is the Prevalence of Trypophobia?
The precise rate of trypophobia is still a riddle. For a long time, this was the wonder that tended to be in the interest of the individuals; presently, it only became clear through the net community and their personal experiences. The information proposes that the number of people perplexed by these photographs is around 10% to 16%, per different overviews. In any case, I would presently like to delve more deeply into the matter. How can we distinguish those with a more articulated, tricky response from those who are just slightly aggravated by such designs?
Ironically, this trypophobia is seen as a world phenomenon that’s special to all individuals of all ages, regardless of their civilization. Even though a few researchers say that ladies may have a better chance of encountering it, it is usually not genuine, and it isn’t the case that a small number of individuals may have it. Still, the ground for these contrasts isn’t clarified, but it is one of the issues in research that’s just rising. Trypophobia is likely underrated since it could be a wonder that seldom comes out in unmistakable shapes that require medical help.
Causes
Shockingly, the researchers have not obtained sufficient proof to clarify trypophobia. Other than the fundamental reasons, the analyst seems to interface a few of the patients’ fears to traumatic encounters, which are normal for all fears. The primordial motivations that are an item of advancement bring out fear in us, and this clarifies why trypophobia is distinctive from other fears. The visual stimulus hypothesis, which is broadly acknowledged, is that our predecessors responded to a few visual stimuli as if they were a signal of threat. There’s a plausibility that the poisonous animal’s skin designs, which are also brilliant and resemble a chemical surface with too many gaps, could be ascribed to trypophobia, which may result from gnawing. One may contend that the brain related these designs with peril and actuated the defensive framework.
The creator considers trypophobia as a fear-repulsion response. The brain may decipher chaotic designs as signs of ailment, deterioration, or contamination that individuals have been conditioned to maintain a strategic distance from. Do you struggle to deal with spoiled nourishment or a new skin infection? These visuals are accompanied by a capable “Don’t touch!” response. Individuals with the same disarrangements may, too, have a brain that sends the same signal to safe designs like honeycombs or sponges.
Another plausibility is that trypophobia is one of the ways the brain forms visual stimuli. A few thought that their spirits or minds permitted them to see as if they were designs or contrasts. This can clarify the failure to hold totally differing convictions when the visual introduction is solid.
Warning Signs and Symptoms
Trypophobia, for case, can have exceptionally gentle side effects, like just a slight fear or exceptionally genuine indications, such as a full-blown freeze assault. Looking at a lotus case can trigger a few individuals to begin, considering they have insects on their skin. Others may indeed have tachycardia by just looking at a bunch of gaps. The witnesses respond instantly, like a wave, and they don’t have sufficient time to think about what they have seen.
Trypophobia is associated with nausea, torment, or fear. The pitiful reality is these can be the foremost extreme shapes in a few individuals, and these feelings can be frozen with side effects like sickness, intemperate sweating, tipsiness, and a dashing heart. There are times when trypophobic individuals will not go to certain places or do certain things in case they think those places or things might have trypophobic triggers. The reason is that the impact of these stimuli can be serious. A picture of being cared for can worsen and become a greater issue when the stress influences the standard of living.

Complications
Although there are no physical threats involved, trypophobia could still have psychological and emotional weight. The most serious risk that people with severe forms of trypophobia face may be the development of avoidance behaviors. Picture a scenario where you are such a revulsion with imperfections that you begin to avoid places where they might exist. The first impression might be that it is a small matter. For instance, you might have refused certain pictures that contain certain words and images. Social limitations at work may arise from this. It is a great risk for the development of depression or the escalating of already existing anxiety disorders the solitude with this distress brings.
Moreover, if the phobia is incessantly activated, the body may develop adverse responses. Accumulated tension promotes hypersensitivity that, in turn, generates hypertension and arrhythmia, along with disruption of sleep patterns. These diseases play a vital part in the development of coronary artery disease and chronic fatigue syndrome. Trypophobic children and teenagers might face difficulties in social or academic settings since they are expected to avoid their triggers. Peer-related or educational problems might arise from this.
Diagnosis
It isn’t easy to analyze trypophobia since it does not have a clear determination in DSM-5, the direct utilized by clinicians and therapists to distinguish mental well-being conditions. The non-appearance of exact directions results in the trypophobia determination being essentially the patient’s depiction of their indications and the doctor’s subjective assessment.
Initial Conclusion
Amid the conclusion, the advisor regularly conducts an in-depth meeting to get data concerning the patient’s past encounters with the issue. At that point, they will ask, for case:
What kind of pictures or occasions do you discover exasperating? And, in what way do these emotions meddle together with your life?
Visual Stimulation
The visual incitement test can be the means by which mental well-being specialists enormously increment the exactness of the conclusion of trypophobia. Pictures appear to the individual, a few of which contain concentrations of crevices or designs known for trypophobia. At that point, the specialists assess the patient’s mental and physical reactions, checking for signs of anguish, fear, or appalling. Consequently, caution is critical when showing the individual exasperating pictures since something else might irritate the indications.
Cognitive-behavioral Assessment
Another imperative strategy of determination is the cognitive-behavioral assessment. It makes a difference to review the feelings and contemplations regarding the person’s response to trypophobic stimuli. For instance, an individual may have the irrational belief that these surrenders show a genuine peril or defilement, even when they know there’s no genuine danger. Recognizing these cognitive inclinations is one of the key components in creating viable treatment.
Treatment
According to Trivia Confidence, “going through a controlled and safe confrontation with the people about their fears ” is a technique called cognitive behavioral therapy.
CBT
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) identifies and teaches individuals how to resist the harmful cognitive processes that are responsible for anxiety. An individual who has trypophobia might picture images with holes and change them in such a way that they do not scare him. Children may interpret them as neutral or interesting rather than scary or ugly.
Exposure Treatment
Exposure treatment is a fundamental part of cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) that is practiced positively by gradually introducing individuals to their triggers in a safe and controlled environment. The aim is to make the person desensitized to the stimuli that trigger their trypophobia by exposing them to low-intensity stimuli. To high-intensity stimuli, and finally, to teach them fear management techniques.
Systematic Desensitization
Systematic desensitization is a method used to treat anxiety similarly to exposure treatment. This therapy begins with relaxation techniques and then exposure to the triggers. Before being shown the pictures, patients may use deep breathing or muscle relaxation techniques to clear their minds and calm their bodies. That makes it possible for people to relate past fearful events to a feeling of calm rather than dread. The target is to reprogram the mind to perceive these cues as non-threatening.
Medications
Medication plays a very important role, especially in panic situations that are accompanied by trypophobia or when the emotional reaction is so strong that it interferes with daily life. Doctors usually recommend antidepressants like SSRIs or benzodiazepines along with treatment to reduce anxiety. On the other hand, medication is typically used as an adjunct rather than a primary treatment.
Exposure Therapy
Exposure therapy is a fundamental approach for treating phobias like trypophobia, which involves the gradual exposure of the patient to their triggers. For example, this technique is similar to using desensitization, which diminishes an individual’s terror response by stepwise intensifying the stimuli.
Cognitive Restructuring
Cognitive restructuring is the main part of cognitive-behavioral therapy, in which the therapist teaches the client to question their wrong beliefs about trypophobic stimuli. The objective is to help the individual see that these patterns do not constitute a genuine threat and may be perceived as neutral.

Prognosis
Treatment for trypophobia appears promising results. Some people have experienced a decrease in treatment-induced indication seriousness with the assistance of cognitive-behavioral treatment and exposure. Numerous patients can bargain with their sentiments and live a typical life without the fear that tormented them for a long time with time and instruction.
Untreated trypophobia causes stress and evasion, hence making it troublesome to achieve everyday assignments. Individuals, without help, may maintain a strategic distance from occasions that put them on edge, confining in their environment. Essential issues like fear of the obscure and stress complicate recuperation.
Prevention
Trypophobia’s capriciousness makes treatment troublesome. Fears require early consideration. Conversely, guardians or caregivers should seek mental well-being help for a kid who unequivocally responds to stimuli.
Psychotherapy could be a conventional strategy that channels fear in a way to dodge the improvement of mental disorders. Relaxation procedures, such as mindfulness, stress administration, and workouts, are viable in diminishing uneasiness. Stretch lessening can contribute to the reduction of phobic responses.
Even though trypophobia can be unavoidable, practicing great mental well-being propensities will help to reduce anxiety-related issues.
This issue is still being examined, but the more data given about its roots and medications, the better the treatment of trypophobia will be.
Sources
- NIH. (2018). Trypophobia: What Do We Know So Far? A Case Report and Comprehensive Review of the Literature.
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC5811467/ - NIH. (2017). Trypophobia: an investigation of clinical features.
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC7111417/ - NIH. (2024). Is trypophobia real?
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38362941/