Even though the lion’s share of individuals request scheduled dental examinations from their common professional, periodontists are prepared to address more complex issues.
Within the field of oral well-being, they work as field operators in observation, reliably watchful in distinguishing the fundamental causes of gum malady. Dental professionals experience a postgraduate preparation program that spans a long time. They look at the complex elements of the mandible and tissues that bolster your teeth amid this time. Counsel a periodontist on the occasion of periodontal issues or in reaction to any anomalies observed by a dental specialist.
What is Periodontology?
The ponder and treatment of clutters that influence the gums and other supporting dental components within the mouth are alluded to as periodontology. That’s associated with watching the mechanical structure that supports your grin. Verbal periodontology is the logical examination of periodontal clutters, which includes their anticipation, diagnosis, and treatment. The dental structure may be mortally obliterated as a result of periodontitis, a more serious frame of gingival irritation. Gingivitis could be a mellow pointer of gingival inflammation. In serious stages, gum illness can influence the gums and other delicate tissues. Furthermore, it may jeopardize your dental well-being, mandible, and, by and large, well-being.
Periodontology is the creative and academic aspect of treating periodontal infection and embedding manufactured teeth. Master periodontists are experts in the inclusion of mandibular dental inserts within the handle for repairing wrong teeth. Counterfeit dental roots are comparable to dental inserts.

What is the Difference Between Periodontists and Dentists?
There are a few key contrasts between these two sorts of masters:
Scope of Specialization
Corrective, remedial, and preventative dentistry are among the essential medications performed by common dental specialists. Periodontists, on the other hand, conduct broad inquire about in order to find and treat gum malady and other related issues surgically. Their essential objectives are to extend tooth quality and reestablish ideal gum well-being.
Training
The as it were distinction between a routine dental specialist and a periodontist is that the last mentioned gets extra instruction in periodontics, which incorporates both surgical and nonsurgical methods.
Domains of Mastery
Whereas most dental practitioners give great dental and gum care, they may refer patients to periodontists for more complex surgical operations or modern gum infection medications.
Types of Methods
Periodontists are the favored pros for gum surgery, scaling, root planing, bone uniting, dental embed addition, and conventional dental strategies like fillings, crowns, and bridges. Dental specialists perform essential dental operations such as fillings and cleanings.
Periodontists control serious gum illnesses and perform particular surgical methods. Both common dental specialists and periodontists play an imperative part in guaranteeing great dental well-being. When standard dental practitioners analyze gum conditions that require more complex treatment, they generally refer patients to periodontists.
Who Should See a Periodontist?
It is prescribed that people look for the administration of a periodontist when they start to show indications of periodontal disease; however, a few people may not require their administration. Who is dependable for planning the consequent dental arrangement? Tireless terrible breath amid brushing and flossing, in expansion to ruddy, puffy, or promptly bleeding gums, may show a more extreme basic condition. Gum retreat, or a broken tooth, is another marker of the continuous partition of the gums from the teeth.
The probability of creating a periodontal malady is expanded by the coexistence of diabetes and cardiac malady. Tobacco utilization is, however, another potential unfavorable result. Moreover, your jaw and aviation routes are influenced. It is prudent to prioritize your gums due to the requests of your plan, as the pressure can, too, have a negative effect on gum well-being. Common dental practitioners will refer patients to periodontists when they watch a compounding periodontal malady or another issue that requires particular treatment.

Diagnostic Methods
Periodontologists run a battery of symptomatic tests to assess teeth and gums. These tools empower them to assess your dental condition more comprehensively and choose the most excellent course of action should any issues be found.
Doing a Patient’s Check
Any periodontal check-up begins with a comprehensive clinical assessment. By now, the periodontist will have inspected your teeth and gums to look for any issues, such as gum retreat or swelling, that may be causing you inconvenience. A periodontal test may be a tiny, abrasive instrument for finding the gaps within the gums around your teeth. On the off chance that your pockets are enormous, they might point to a periodontal malady; if they are profound, a disease can be displayed.
Radiographic Evaluation
Dental diagnosis of gum disease depends on X-rays. They empower the periodontist to see issues emerging underneath the skin, which is found beneath the surface of the bone. The periodontist finds that the gum disease is progressing as the X-rays show no bone. Separated from self-evident issues, X-rays offer assistance in discovering concealed ones like abscesses or tumors.
Periodontal Charting
Looking at your gums’ condition is like periodontal observation. Part of the method must incorporate documentation of estimations from the clinical test, counting gum take profundity, bleeding nearness, and gum recession amount. This careful record helps the periodontist screen any conceivable changes in your gum condition over time.
Microbial and Biochemical Examination
In some cases, it is essential to discover the particular bacterium causing gum infection and start with microbiological testing. To assist them in identifying microscopic organisms, periodontists send tests of plaque or gum fluid to a lab for genetic testing. When conventional treatments fail, distinguishing the precise bacterium causing the infection can help supply more concentrated treatment.
Molecular Gene Research
Hereditary testing can be useful under a few circumstances. This test approximates your chance of gum illness by utilizing your genetic makeup. A few people are basically more likely to have these issues than others, indeed with the foremost strict dental cleaning plan. Based on your family’s gum illness history, a periodontist can propose preventative care to assist and protect the well-being of your gums.
Treated Health Problems
Progressed periodontics professionals can distinguish and oversee a wide range of gum and tooth issues, from the most basic to the most complex. The following are among the foremost squeezing concerns they handle.
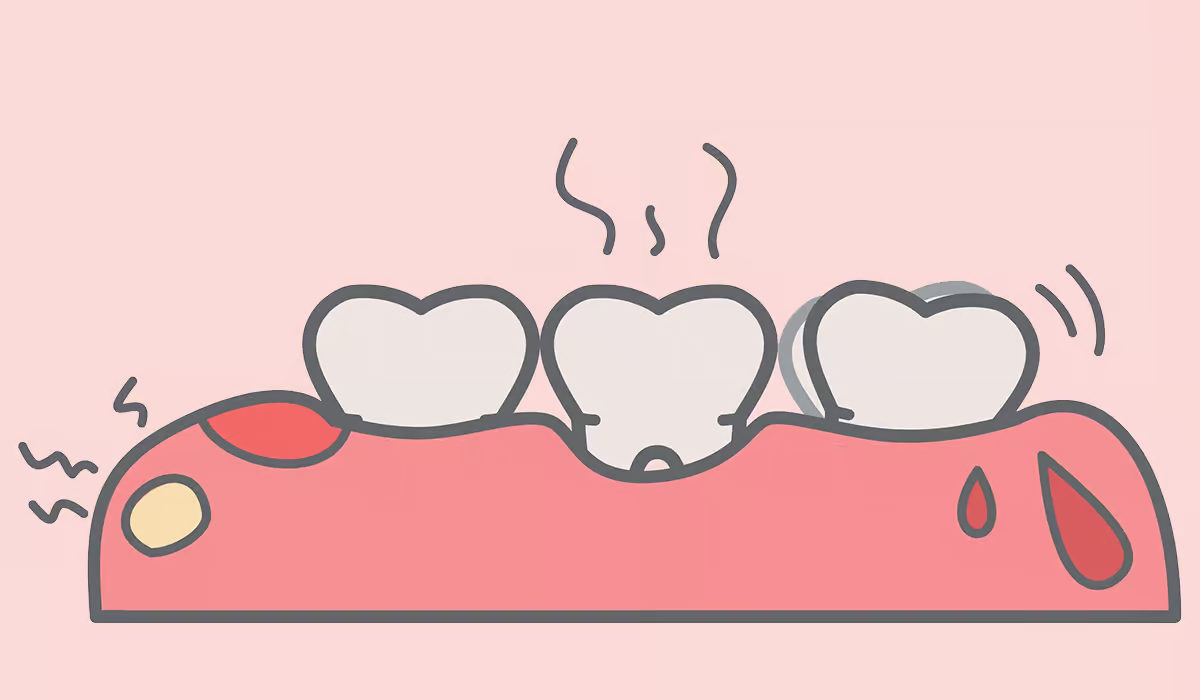
Gingivitis
The primary sign of periodontal malady is the nearness of gingivitis. Statement of plaque on the gums and teeth can cause dental torment. After the drawn-out presentation to brushing or scouring, one may take note of the nearness of ruddy, swollen, and bleeding gums. Effective administration of gingivitis can be accomplished by following legitimate verbal cleanliness hones and frequently planning master dental cleanings. In case cleared out untreated, periodontitis can advance to periodontal malady, requiring therapeutic activity. Periodontal pros do exhaustive dental cleanings of the teeth and gums to address gingivitis and offer patients information on how to care for their teeth at home.
Chronic Periodontitis (CP)
The foremost lethal sign of periodontal malady is incessant periodontitis. This condition influences both the buccal tissue and the osseous system that bolsters the teeth. Periodontal malady leads to the improvement of tainted cavities when the gums experience subsidence from the teeth. In reaction to the disease, the body starts the method of disintegrating the hard and osseous tissues that give support to the teeth. Scaling and root planing is an orderly cleaning technique periodontists use to kill gum pockets around teeth and manage repeating periodontitis. Any sustained damage may last unless surgical mediation is carried out.
Aggressive Periodontitis
Within periodontal illness, forceful periodontitis is recognized by its quick progression and the frequent signs of early tooth loss. Whereas periodontitis is broad in common, cases of constant periodontitis are to some degree uncommon and, for the most part, affect more youthful people. This condition can be ascribed to hereditary contrasts, frequently related to a specific strain of microbes. Extreme forms of periodontitis may require surgical intervention, the organization of antimicrobials, or comprehensive tooth scaling.
Periodontal Abscess
A periodontal abscess is the result of gum infection showing in conjunction with serious torment. Discharge could be a gooey liquid shaped when microbes get caught within the interdental crevices between the teeth and gums. Conceivable clinical signs incorporate torment, edema, and an unsavory lingering flavor. The periodontist will oversee the abscess by carefully evacuating the pus, thoroughly cleansing the influenced zone, and endorsing pharmaceuticals on the off chance that it is required. Additionally, they will handle any crucial issues that have played a part in improving the blister.
Gum Recession
When the gums peel off, the roots of the teeth can be seen. That’s called gum recession. A few things, like periodontal illness, not brushing your teeth legitimately, and a hereditary inclination, can make this issue more awful. Roots uncovered for a long time can become weaker and more likely to decay. Periodontists utilize gum joins to cover up bone roots that appear when the gums retreat. The exact portion of the mouth range from which the tissue comes is obvious.
Dental Implants
Periodontists regularly do great work of putting in tooth implants. Are you losing teeth and require a modern tooth? In the long run, an embed may be the best option. Dental inserts are small metal gadgets that work like natural tooth roots after being surgically set within the jaw. Once the embed has been set accurately and intertwined sufficiently with the bone, a cap can be put on the best of it. The conclusion result of this treatment may be a tooth that works superbly once more. Experts within the restorative field called periodontists are specialists at putting in tooth inserts and making, beyond any doubt, stay steady with standard medications.

How To Prepare For a Visit?
To induce the finest treatment, make sure you’re prepared for your visit to the periodontist ahead of time. Check out the following ways to induce preparation.
Accumulate all of your dental data, such as X-rays, records of past visits, and records with notes added to them. Your periodontist can use this information to learn more about your mouth health and any issues associated with it and see if you’ll be able to deliver a proposal from your fundamental dental practitioner.
During the time before the assembly, attempt to remember any signs you have had. Can you see any redness on your toothbrush? Is there any torment amid rumination? Compose them down, together with any questions or stresses you’ll have. It’s best to do these things to have a productive discussion with your periodontist and get all of your questions answered.
Don’t eat or drink anything other than water for at least one hour before your arrangement. These tips will help you keep your teeth clean within the days before the test. In case your periodontist doesn’t tell you something else, take your drugs precisely as suggested.
Finally, please make sure you get there on time. After you see the periodontist, they will take estimations, get X-rays, or do other therapeutic tests as a portion of a full assessment. It’s vital to be on time so that there’s sufficient time for a full check.
Sources
- AAP. What is a Periodontist?
https://www.perio.org/for-patients/what-is-a-periodontist/ - NIH. (2013). Periodontal Research: Basics and beyond – Part I (Defining the research problem, study design and levels of evidence).
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3808007/ - WDC. (2024). What is Periodontology and What Does a Periodontologist Do?
https://warsawdentalcenter.pl/en/what-is-periodontology-and-what-does-a-periodontologist-do/