Typical signs of an allergy are often rhinitis (a persistent runny nose), hives, and itchy skin conditions. However, allergy reactions vary greatly in different people and substances. It ranges from mild inflammation to a life-threatening reaction known as anaphylaxis.
Most allergies can’t be cured. However, there are effective treatments that relieve symptoms and provide comfort to people with immune system hypersensitivity. If a person has a severe allergic reaction, the doctors use epinephrine – a life-saving medication to stop the reaction to the allergen.

How Common Is It?
Allergies are very prevalent. According to the CDC, more than a quarter of United States citizens have at least one allergy. According to those data, over 25% of adults have a seasonal allergy, and around 6% have a food allergy.
Among children, boys are more likely to get seasonal allergies than girls.
Types
Foods Allergies
A food allergy happens when you eat a particular food that your body recognizes as a harmful substance and launch an immune reaction against it. The severity of the reaction ranges from mild to severe, and it is essential to remember that it isn’t always the same. If you experience mild reactions to a particular food, it doesn’t mean that the allergic reaction will look the same next time – it can become more severe.
The most common food that triggers allergic reactions include:
- Peanuts
- Shellfish
- Milk
- Eggs
- Wheat
- Soy
- Strawberries
- Tree nuts
- Fish
- Sesame
Food allergy symptoms include nausea, vomiting, hives, itching skin, and swelling (edema) in the mouth area (tongue, face, and throat).
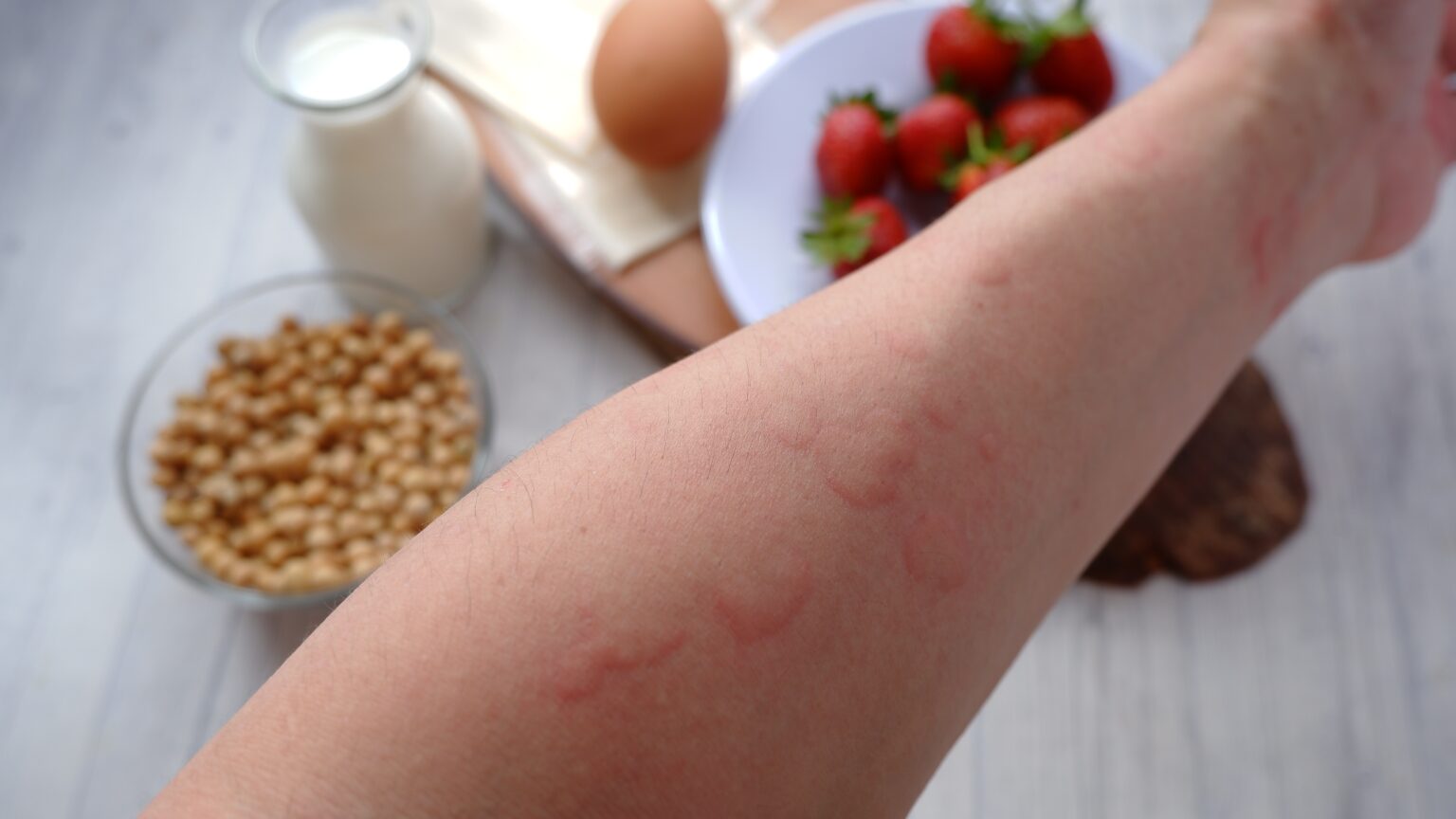

Inhalants
Inhalant allergies occur when the substance to which your body overreacts is consistent with the air you breathe. It includes seasonal allergies and allergies that happen throughout the year. Allergens that may cause this type of immune system overreaction include:
- Pollens – Pollens cause seasonal allergies. They are powdery substances that are produced by flowers of seed plants. It is transported by the wind from plant to plant to fertilize plants. Different species of trees release pollen at different times of year. If you notice seasonal allergy symptoms, it may be helpful to note the time of year it occurred.
- Dust mites – Microscopic creatures known as dust mites survive on the expired skin cells of humans. Common living quarters for these critters include material objects such as bedding mattresses, carpets, or pillows due to their propensity towards collecting dead skin detritus.
- Pets – Pets may sometimes be the culprits behind human allergies. The proteins in their fur, saliva or skin can trigger an irritating reaction. Animals that mainly cause reactions in people are cats and dogs. While some animal breeds (e.g., poodles, some terriers, and Portuguese water dogs) are considered “allergen-free,” experts don’t recognize any pet as 100% allergen-free.
- Molds – Molds are a type of fungi that release to the air spores in the form of pollen. Mold allergies are most commonly caused by Aspergillus and Cladosporium molds in humans.
Inhalant allergy symptoms include rhinitis, nose itch, sneezing, and watery, itchy, and red eyes (conjunctivitis).
Latex
Latex is a natural rubber acquired from the sap of the rubber trees growing in Africa and South Asia (Hevea brasiliensis). However, natural rubber latex should be distinguished from synthetic latex produced by chemicals that do not cause allergies in humans.
Latex allergy can develop after repeated exposure to latex. Keep it in mind when you develop contact allergy symptoms – the fact that you used latex products in the past without developing an allergy doesn’t confirm you are not allergic.
Latex products include:
- Disposable gloves
- Condoms
- Rubber toys
- Balloons
- Baby bottles
- Tires
- Athletic shoes
- Pacifiers
- Bandages
- Syringes
Symptoms of latex hypersensitivity are most commonly contact dermatitis, a skin rash that appears on the site of skin that had contact with latex products. It usually develops in a few minutes from skin contact with latex. Less common symptoms include a runny nose, itching, hives, difficulty breathing, and a fall in blood pressure (shock).
Insects Stings
When a human is stung by an insect, it may release venom under the skin. Venom is a substance that can cause an immune system reaction. Most people don’t have allergic reactions after being stung by an insect or having a mild one. Severe, life-threatening reaction is estimated to affect up to 0.8% of children and 3% of adults.
In the United States, there are five known insects whose venom can cause an allergic reaction after the sting. These are:
- Honeybees
- Wasps
- Hornets
- Yellowjackets
- Fire ants
Symptoms of insect sting allergy include:
- Swelling and redness around the site of the sting
- Hives
- Pain
- Itching
- Flushing
- Dizziness
- Wheezing
- Swelling inside the mouth or throat, swallowing difficulties (when the sting site is inside of the mouth or throat)
- Anaphylaxis – happens rarely. Symptoms of anaphylaxis include breathing problems, a drop in blood pressure (shock), and a rapid heart rate.
If you are diagnosed with an allergy to insect venom or have had anaphylaxis in the past, you will probably be prescribed self-injected epinephrine. Remember to carry it with you at all times for emergency rescue.
Medications
Certain medication substances can cause allergic reaction symptoms in some people. This happens when your immune system recognizes those substances as a threat and reacts against them. It can concern all types of drugs – over-the-counter medications (OTC) and prescription ones. Also, any form of the drug can lead to hypersensitivity – pills, liquid, topical, or injectable form.
Medications that most commonly cause allergies include:
- Certain antibiotics
- Insulin
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen and aspirin
- Chemotherapy drugs
- Anticonvulsants
Drug allergy symptoms include skin rash, itching, hives, wheezing, breathing problems, drop in blood pressure, swelling, dizziness, and vomiting.
Remember to always tell doctors about your drug allergies. Even if they don’t plan to prescribe you medication you’re allergic to, it is essential to mention your drug intolerances since having an allergic reaction to certain drugs may raise your chances of having it in response to some others.
Causes
Many different cells of the immune system and the substances they produce are involved in the body’s response to allergens. Cells of the immune system, including eosinophils, mast cells, lymphocytes, and antibodies – immunoglobulins E (IgE), protect the body against threatening factors, e.g., microorganisms. Sometimes, however, these cells recognize harmless allergens as dangerous and initiate a response leading to the patient’s sensitization.
Initially, the allergen is recognized by dendritic cells. They present them to cells called T lymphocytes, which regulate the functioning of the immune system, which in turn instruct B lymphocytes to produce antibodies, the so-called immunoglobulins E. The tendency to make IgE is hereditary, i.e., genetic. Diseases in which IgE immunoglobulins play the leading role are called IgE-dependent.
Immunoglobulin E, combined with mast cells found in the patient’s tissues, stimulates them to secrete substances, including histamine and causes the influx of many inflammatory cells. This, in turn, causes allergy symptoms.
Common substances that trigger allergy (allergens) include:
- Pollen
- Animal dunder
- Mold
- Dust mites
- Particular foods, including peanuts, milk, soy, shellfish, and wheat
- Bee venom
- Medications, such as penicillin
- Latex, which can cause skin allergy reaction
Risk Factors
Some people are at a higher risk of having allergies. The risk factors include:
- Family history of allergies (hay fever, eczema, or hives)
- Family history of asthma
- Being a child
- Having asthma
- Already having some allergy
Experts found risk factors that also raise the risk of severe reactions. Those include:
- Asthma
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
- People with cardiac conditions and hypertension
- Intestinal lung disease
Symptoms
Symptoms of allergies depend on their causes. Also, the severity of body reactions to the allergen ranges from mild to life-threatening.
Hay Fever
Allergic rhinitis, also called hay fever, causes symptoms such as:
- Runny nose
- Sneezing
- Coughing
- Conjunctivitis – red, watery, and swollen eyes
- Nose itch
- Itching of the eyes
- Headache
- Pain
Food Allergy
Food allergy symptoms can involve the gastrointestinal, skin, cardiovascular, and respiratory systems. Symptoms may include:
- Nausea and vomiting
- Stomachache
- Hives
- Dizziness
- Shortness of breath
- Wheezing
- Rapid pulse
- Pale color of skin
- Anaphylaxis
Insect Sting Allergy
Bug bites can have different effects on different individuals. An intense localized reaction might go beyond the site of the sting, leading to a larger area of itchiness and redness. Symptoms of insect sting allergy include:
- Pain at a sting site
- Redness and swelling (edema)
- Hives
- Itching
- Cough
- Wheezing
- Shortness of breath
- Tightness in the chess
- Hoarse voice
- Tongue swelling (if a sting occurred in the mouth area)
- Difficulty swallowing
- Anaphylaxis
Drug Allergy
Symptoms of a drug allergy may include:
- Hives
- Skin rash
- Wheezing
- Itching
- Swelling
- Dizziness
- Vomiting
- Anaphylaxis
Sometimes, the first time you take medication you’re allergic to, you may not experience allergic reaction symptoms. However, your body produces antibodies to this specific substance that will cause symptoms the next time you take it.
Anaphylaxis
Anaphylaxis is a swift and potentially fatal hypersensitivity response triggered by certain elements such as food, medication, or venom from bee stings. This reaction typically induces blood pressure to drop dramatically, resulting in shock. For the majority of individuals experiencing anaphylactic reactions – skin rashes, also known as hives, often show up before anaphylaxis after consuming particular foods or medications.
Dangerous symptoms include:
- Dizziness
- Loss of consciousness
- The feeling of severe weakness
- Weak, rapid pulse
- Palpitations
- Hoarseness
- Cough
- Shortness of breath
- Nausea and vomiting
- Abdominal pain.
Diagnosis
There are several types of tests for allergies. The most common ones are:
- Skin prick tests (scratch tests) – during that test, a medical professional pricks your skin several times with tiny amounts of proteins from common allergens. If you’re allergic to any of them, your skin will develop a small raised bump, also called a hive, at the site where you have been pricked.
- Blood test – another allergy test is a blood test for immunoglobin E (IgE). The level of antibodies that cause allergy symptoms is measured in that test. However, blood tests are not as sensitive as prick tests.
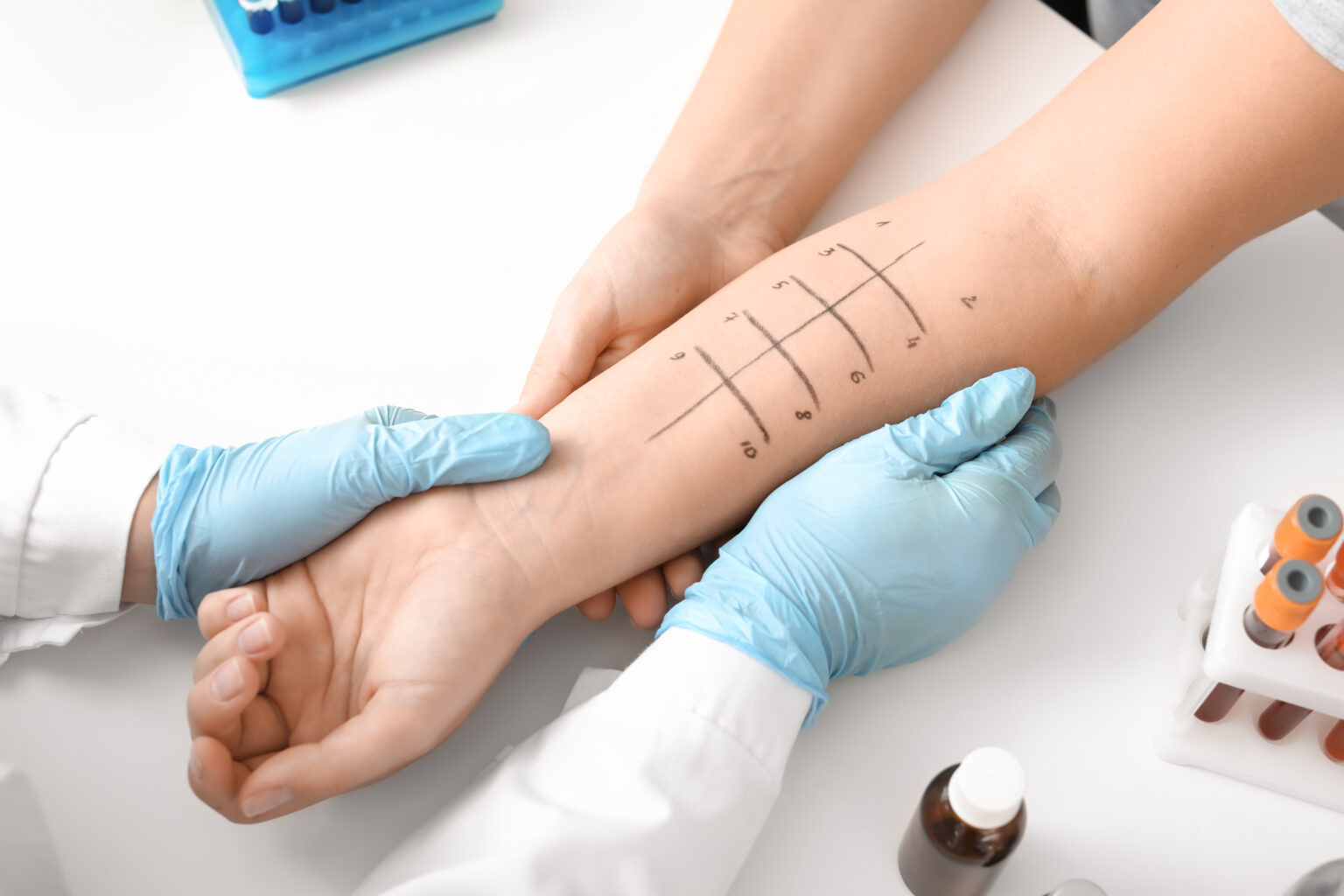
Treatment
If you have an allergy, the first thing you can do is avoid the allergen that causes it. However, in the case of pollens, dust mites, and other inhalant allergies, it may be impossible to avoid allergens altogether. In that case, OTC or prescription medications may be necessary.
Treatment for allergies includes:
- Medications: antihistamines, steroid creams, and steroid pills
- Epinephrine auto-injectors are used for emergency rescue in the case of severe, life-threatening reactions called anaphylaxis.
- Immunotherapy, also called desensitization – this procedure should be done by medical professionals and is recommended for people with severe reactions. It consists of exposing you to the substance you’re allergic to carefully and gradually so that your body gets used to it and reacts less severely when contracting it.
The specific treatment choice should be discussed with the doctor as every person’s allergy may be managed differently.
Prevention
The most effective allergy prevention method is avoiding things you’re allergic to. When you can’t avoid contact with allergens altogether, try to minimize it as much as possible.
Vacuum your rugs and carpets regularly to remove dust mites, pollens, and animal dander. Changing your sheets weekly is best if you are allergic to dust mites.
It’s a good idea to wear a medical alert bracelet if you have experienced severe reactions so that others can know you have an allergy and quickly assist you if needed.
If you have a food allergy, remember to ask if the meal you’re ordering in the restaurant is free of the food you can’t eat. Even if it doesn’t seem to contain it at first, some sauces can have peanuts in them, so it’s best to let the waiter know about all your food allergies.
When Should You See a Doctor?
If you notice any symptoms of allergies, such as runny nose, skin rash, itching, or sneezing, you should consult your doctor, who may run a further diagnosis and implement treatment. The doctor who diagnoses and treats allergies is called an allergist.
Call an ambulance immediately if you experience symptoms of a severe reaction, such as breathing difficulties, wheezing, dizziness, and a drop in blood pressure.
Sources
- National Library of Medicine (NIH) Joseph M. Dougherty; Khalid Alsayouri; Adam Sadowski. Allergy (2023) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK545237/
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) More Than a Quarter of U.S. Adults and Children Have at Least One Allergy (2023) https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/pressroom/nchs_press_releases/2022/20220126.htm
- National Health Service (NHS) Hay Fever (2021) https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/hay-fever/
- American College of Allergy, Asthma, & Immunology (ACAAI) Food Allergy (2023) https://acaai.org/allergies/allergic-conditions/food/
- American College of Allergy, Asthma, & Immunology (ACAAI) Insect Sting Allergies (2018) https://acaai.org/allergies/allergic-conditions/insect-sting-allergies/
- National Library of Medicine (NIH) Kevin McLendon; Britni T. Sternard. Anaphylaxis (2023) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK482124/
- American College of Allergy, Asthma, & Immunology (ACAAI) Latex allergy https://acaai.org/allergies/allergic-conditions/latex-allergy/
- American College of Allergy, Asthma, & Immunology (ACAAI) Drug allergies (2018) https://acaai.org/allergies/allergic-conditions/drug-allergies/
- National Health Service (NHS) Allergies (2022) https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/allergies/